Red Eyes Outbreak in Uganda: What To Do
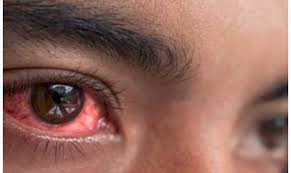
In recent weeks, Uganda has been grappling with a concerning outbreak of red eyes, a highly contagious condition that has affected communities across the country.
In March, the Ministry of Health confirmed an outbreak of Conjunctivitis, commonly known as red eyes disease, with hundreds of cases diagnosed in affected schools and prison facilities in the country.
Cases of red eyes have increased eight times from 954 on March 14 to 7,596 cases by April 6. The majority of the 5,897 cases were reported by prisons across the country, with schools registering 700, communities 658, health centers 266, and police stations 75. A total of 382 suspected cases were screened and managed, of which 297 cases were detected at the Nimule point of entry and 85 other cases at Nimule hospital.
Within a month, Uganda reported over 7500 cases of red eye infections across the country.
Over 500 students admitted in various health facilities to receive treatment.
Affected institutions included schools in Kampala and eight prison facilities, including Luzira Upper Prison, Murchison Bay Prison, Kassanda Prison, and Kaweeri Prison, among others. The outbreak also spread to communities in Kagadi, Wakiso, Mukono, Arua, Masaka, Luwero, and beyond.
Despite the widespread occurrence, the Ministry reported a recovery rate of 90% among affected individuals.
Emmanuel Ainebyoona, Ministry of Health spokesperson, recently said that while the outbreak garnered attention, it is not considered a major concern. He likened the ailment to a common flu within a family, stating that it is a self-limiting disease that requires discipline in management.
Ainebyoona emphasized the importance of adhering to hygiene guidelines, such as avoiding the sharing of personal belongings with infected individuals and practicing frequent handwashing.
“This is a self limiting disease that is comparable to when someone in the family has flu. It is not among the diseases of concern to us as the Ministry of Health and its going to clear , all people need to do is follow the guidelines on hand hygiene and this will help us control the infection” he said



Comments are closed.