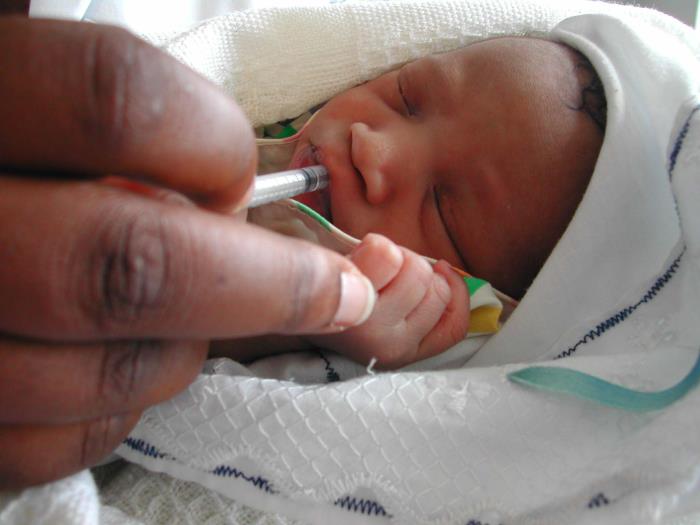
Uganda has made significant strides in the efforts against HIV/AIDS particularly reducing the number of babies born with HIV from 310,000 in 2010 to 28,000 in 2011, figure that now stands at 4,600, records from the Uganda AIDS Commission (UAC) show.
In a message shared on the UAC twitter handle, Uganda now becomes one of the first countries in Africa to register a reduction of mother to child transmission of HIV.
“UG is one of the 1st countries in Africa to register a reduction of mother to child transmission of HIV. MTCT has dropped from 310,000 in 2010 to 28,000 in 2011 and is now at 4,600 in 2016. Maternal to Child transmission of HIV has been reduced by 87%,” reads the tweet.
This means that mothers living with HIV have heeded the government call to follow measures that ensure an HIV free baby.
The government through her various health agencies has always urged positive mothers to seek and follow healthcare provider’s advice before conceiving and throughout pregnancy.
The Word Health Organisation recommends that HIV-positive mothers or their infants take antiretroviral drugs throughout the period of breastfeeding and until the infant is 12 months old. This means that the child can benefit from breastfeeding with very little risk of becoming infected with HIV.